1. The variations in enthalpy that can not be detected per calorimeter can be detected with the aid ofNewton’s lawHess’s lawKrebs lawOhm’s law2. The energy required to sever a given covalent bond is namedbond energybond enthalpybond dissociation energyall of above3. Changes in enthalpy ...
1. The variations in enthalpy that can not be detected per calorimeter can be detected with the aid of
- Newton’s law
- Hess’s law
- Krebs law
- Ohm’s law
2. The energy required to sever a given covalent bond is named
- bond energy
- bond enthalpy
- bond dissociation energy
- all of above
3. Changes in enthalpy in an exothermic reaction is
- positive
- negative
- constant
- neutral
4. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can not be
- created only
- destroyed only
- converted
- created and destroyed
5. Hess’s law states that a chemical reaction is independent of the route by which chemical reactions takes place while keeping the same
- initial conditions only
- final conditions only
- mid-conditions
- initial and final conditions
6. The standard enthalpy change of neutralization involves the reaction of an acid with an alkali to form 1 mol of
- water
- oxygen
- nitrogen
- anhydrous salt
7. The change in the energy between a chemical reaction and the surroundings at constant temperature is called
- enthalpy change
- enthalpy
- enthalpy profile
- dynamic enthalpy
8. To initiate a reaction the minimum energy which is required to break bonds is called
- bond energy
- activation energy
- breaking energy
- ionization energy
9. The standard condition for enthalpy changes are
- the pressure of 100 kPa
- temperature 298K
- normal physical state
- all of above
10. The application of law of thermodynamics to the enthalpy change was done by
- Newton
- Hess’s
- Lewis
- Sophocles
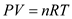 …… (1)
…… (1)
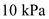 for P,
for P,  for V, 10 mol for n, and 8.31 for R.
for V, 10 mol for n, and 8.31 for R.
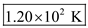 .
.