Faraday's Law of Electrolysis
Before moving into Faraday's Law of Electrolysis, let's talk about electrochemistry and some terms related to it. Electrochemistry The branch of chemistry that deals with the study of relation...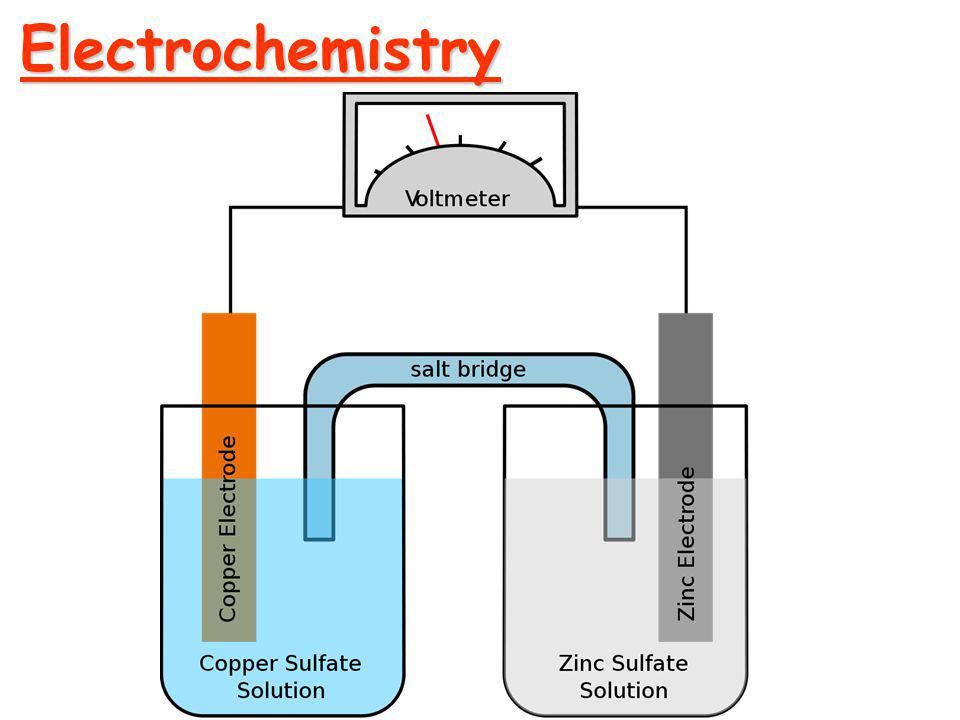

Electrolysis:
The chemical decomposition or deposition of an electroactive substance at the surface of electrode or from the surface of electrode when electric current is passed through the electrolytic solution is known as electrolysis.
To carry out electrolysis, the solution is taken in vessel known as electrolytic vessel or voltameter and two metallic rod or plates are dipped in the solution known as electrodes. These two electrodes are connected to the positive and negative terminal of the battery through a wire. Electric current enters and leave the electrolytic solution through these electrodes.
Electrodes:
The metallic rods or plates or foils through which electric current enter into or leave from the electrolytic solution are called electrodes.
The electrode, which is connected to positive terminal of battery is called a anode and negative terminal of battery is called cathode. During electrolysis cation migrate towards cathode and anion migrate towards anode
Types of electrodes:
There are two types of electrodes. They are attackable electrode and non-attackable electrode.
a. Attackable electrode:
The electrode which itself participate in oxidation and reduction during electrolysis is called attackable electrode. For example, copper electrode, Ag- electrode, Zn- electrode, etc.
b. Non-attackable electrode:
The electrode which itself does not take part in oxidation and reduction during electrolysis is called non- attackable or inert electrode. For example, graphite electrode, platinum electrode, etc.