Faraday's Law of Electrolysis
Before moving into Faraday's Law of Electrolysis, let's talk about electrochemistry and some terms related to it. Electrochemistry The branch of chemistry that deals with the study of relation...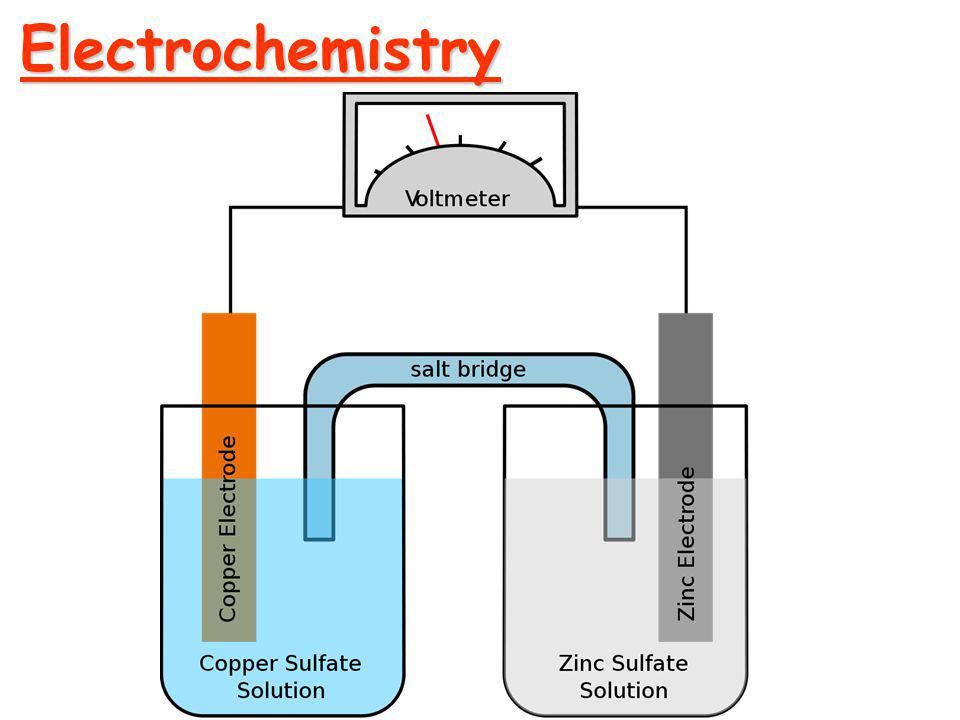

Electrochemical cell
A device which is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy is called electrochemical cell or galvanic cell.
Electrolytic cell
A device which is used to convert electrical energy into chemical energy is called electrolytic cell.
Difference between:
| Electrochemical cell | Electrolytic cell | |
| It is a device which is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy. | i. | It is device which is used to convert electrical energy into chemical energy |
| It is based on spontaneous redox rxn. | ii. | It is based on non spontaneous redox rxn. |
| Two electrodes are set up in different electrolytic solutions. | iii. | Two electrodes are set up in same electrolytic solution. |
| The electrode on which the oxidation takes place is called anode & on which reduction takes place is called cathodes. | iv. | The electrode which is connected to positive terminal of battery is called anode and which is connected to negative terminal of battery is called cathode. |
| Salt bridge is used in electrochemical cell. | v. | Salt bridge is not used in electrolytic cell. |
Electronic
Concept of oxidation & reduction.
1. Oxidation
Oxidation is a half reaction in which the loss of electron or increase in positive charge takes place. The atom or ion which lose the electron is said to be oxidized. The oxidized atoms or ions act as anode in electrochemical cell.
2. Reduction
Reduction is a half reaction in which gain of electron or decrease in positive charge (+ve charge) takes place. The atom or ion which gain electron is said to reduce. The reduced atoms or ions act as cathode in electrochemical cell.
3. Redox-reaction:
A reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously is called redox-reaction. In a redox reaction one of the substance lose electron while the other gains the same number of electrons. Example: Zn + CusO4 ⇾ ZnSO4 + Cu
Oxidation: Zn –2e- ⇾ Zn++
Reduction: Cu++ + 2e- ⇾ Cu

Symbolic representation of an electrochemical cell.
The ways of representation of electrochemical cell are:
i. Single vertical line (|) represents phase boundary which separate the different form of same species.
written on the right from the self-bridge.
respective side.
Electrode potential
The tendency of an electrode to lose or gain electron when it is in contact with its own ionic solution is called its electrode potential and denoted by a symbol" E".
The electrode potential is termed as oxidation potential if oxidation takes place as the electrode with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode and is called reduction potential if reduction takes place at the electrode with respect to standard hydrogen electrode. This oxidation potential or reduction potential is known as single electrode potential.
If the electrode potential measured under standard condition is known as standard electrode potential and denoted by a symbol "E0". The standard conditions are:
iii. Pressure of the gas is 1atm.
Electromotive force (emf) of cell
The force which causes the flow of electron from anode to cathode and result in the flow of current in a circuit is called electromotive force or emf of cell. These forces arise due to the difference in potential between two electrodes.
Thus electromotive force may be defined as the difference of potential between two electrodes which cause the flow of current from an electrode of lower reduction potential to an electrode of higher reduction potential.
The emf of a cell determined under standard condition is called the standard emf and denoted by a symbol E0 cell .The standard conditions are:
i. Concentration of electrolyte is 1M.
ii. Temperature of rxn system is 25ºC.
iii. Pressure of gas is 1 atm.
Reference electrode
The potential of unknown electrode can be calculated by combining (connecting) it with an electrode of known potential in an electrochemical cell. The electrode of known potential which is use to determine the potential of unknown electrode is called reference electrode. For example:
Standard hydrogen electrode, Calomel electrode
Standard hydrogen electrode.
In standard hydrogen electrode, hydrogen gas at 1atm pressure is passed into 1M HCl solution in which platinum metal remains immersed which is shown in a figure below.

The standard hydrogen electrode may act as a cathode or anode when it is combined with experimental electrode. So its notation may be represented as:
i. When it acts as anode then (Pt) H2(g, 1atm)/H+(1M)// Cathodic rxn
or
ii. When it acts as cathode then Anodic rxn // H+ (1M) / H2(g, 1atm) (pt
Difficulties/ disadvantage of standard hydrgen electrode.
It is difficult to maintain unit concentration of H+ ion.
ii.) It is difficult to maintain 1 atm pressure.
Sign convention for electrode potential
when Zn electrode comes in contact with Zn++ ion, these exist an equilibrium between Zn and its ion
i.e.
Zn <=> Zn++ + 2e–
Here forward reaction is oxidation & backward reaction is reduction. The potential developed in forward rxn is oxidation potential & backward rxn is reduction potential. The magnitude of oxidation & reduction potential are same but different in sign.
i.e.
oxidation potential of an electrode = – reduction potential of same electrode