Antiderivatives
Antiderivtaives Antiderivatives are the opposite of derivatives. An antiderivative is a function that reverses what the derivative does. One function has many antiderivatives, but they al...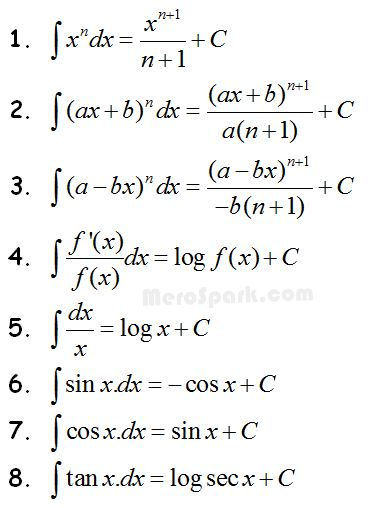

Standard integrals (I)
∫dxa2−x2=12alog(a+xa−x) + C
∫dxx2−a2=12alog(x−aa+x) + C
∫dxx2+a2=1atan−1xa + C
∫dxa2−x2√=sin−1xa + C
∫dxx2−a2√=log(x+x2−a2−−−−−−√)+ C
∫dxx2+a2√=log(x+x2+a2−−−−−−√) + C
Standard integrals (II)
Formula for Integration by parts
∫ (uv) dx = u∫ vdx- ∫ (dudx)∫vdx
∫ eax cosbxdx=eax (acosbx+bsinbx)a2+b2
∫ eax sinbxdx=eax (asinbx−bcosbx)a2+b2
Standard integral of trigonometrical functions:

Integral of hyperbolic function:
∫sinhx dx = coshx+ c
∫ coshx dx = sinhx+ c
∫tanhx dx = ln(coshx )+ c
∫ cotdx = ln|sinhx|+ c
∫ sechx dx= tan-1 |sinhx|+c
∫ cosechx dx= ln |tanx2 |+c
Standard integral (III)
∫dxasinx+bcosx
=1a2√+b2log(tan12(x+tan−1ba))+c