L Hospital's Rule
limx→4x2−16x−4limx→∞4x2−5x1−3x2In the first limit if we plugged in x=4 we would get 0/0 and in the second limit if we “plugged” in infinity we would get ∞/−∞ (recall that a...
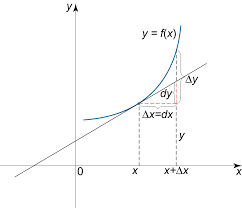
Differentials:
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = f(x) with respect to changes in the independent variable. The differential dy is defined by

where 

holds, where the derivative is represented in the Leibniz notation dy/dx, and this is consistent with regarding the derivative as the quotient of the differentials. One also writes



Tangents and Normal:

Equation of Tangent and Normal:

The angle of intersection of two curves:
