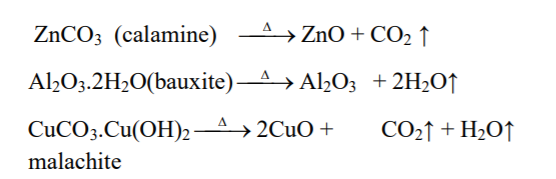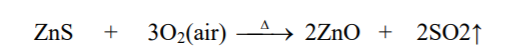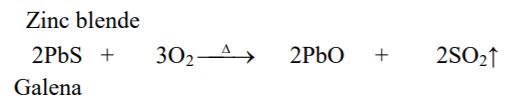↪ The concentrated ore is then worked up for the extraction of the metal by any one of the following methods:
⇲ Calcination and Roasting
⇲ Reduction
⁕ Calcination and Roasting

↪ The concentrated ore is then taken for calcination or roasting.
⇲ Calcination
↪ The process of heating of concentrated ore at a temperature below its melting point in absence or limited supply of air to convert ore into metallic oxide is called calcination.
↪ Calcination is done for oxide, hydroxide, hydrated and carbonates ores.
↪ This process is done in reverberatory furnace or sinterers. 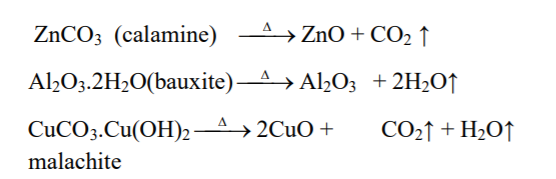
⇲ Roasting
↪ The process of heating the concentrated ore at a temperature below its melting point in presence of excess air to convert the ore into metallic oxide is called roasting.
↪ This process is employed in case of sulphide ore where ore gets converted into the metallic oxide.
↪ This process is also done in reverberatory furnace or sinterers.
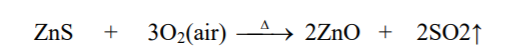
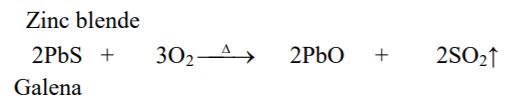
⁕ Reduction
↪ It is a process to reduce metallic oxide obtained from roasting or calcination into free metal by heating with suitable reducing agent or by electrochemical process.
↪ The commonly used methods for reduction are:
⇲ Smelting
⇲ Electrolytic reduction
⇲ Precipitation
Smelting
↪ It is a process of heating of metallic oxide obtained from roasting or calcination in presence of reducing agent and little suitable flux in order to get free metal.
↪ Smelting generally involves
i. Reduction of metal oxide into metal.
ii. Formation of fusible slag.
↪ Depending up on the nature of metal and metallic oxide, following types of methods are used for smelting.
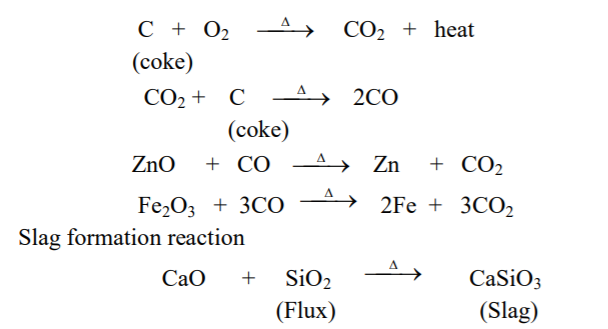
⇲ Carbon reduction
The process of reduction of metal oxide to the metal by strongly heating it with carbon (coke) and a suitable flux in a blast furnace is called carbon reduction.
Metal oxide obtained from roasting or calcination is mixed with coke and a little suitable flux and then heated by applying blast of hot air from bottom of furnace.
Reactions occur as,
⇲ Thermite process or Aluminothermite process
↪ Certain metal oxides like Cr2O3 and Mn3O4 can’t be reduced by carbon reduction process since oxygen has higher affinity with these metals than with carbon.
↪ In such case, aluminum is used as reducing agent.

↪ This process, the roasted or calcined ore is mixed with aluminum powder, a little BaO2 peroxide powder and suitable flux in a crucible.
↪ Then burning magnesium ribbon is introduced in the crucible to start ignition.
↪ Due to production of high temperature, the metallic oxide is reduced into molten metal which collected from bottom and slag remains behind in the crucible.

Electrochemical reduction
↪ The metals which are very reactive such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al etc. are usually extracted by the electrolysis of their fusible salt.
↪ During electrolysis, metal gets deposited at the cathode. For example, Sodium is extracted from fused NaCl by Down’s process.

↪ In this way, sodium is liberated at cathode and chlorine gas is liberated at anode.
Precipitation process
↪ In this process, aqueous solution of the metallic compound obtained from leaching is treated with suitable reducing agent like Zn in order to get precipitate of metal.
↪ This process is also called the wet process of metallurgy.